Statistics at a Glance
At a Glance
Based on estimates of new cancer cases in 2025, 4.2% of all new cases will occur among ages 15 to 39. 86.0% of AYAs diagnosed with cancer will survive their cancer for 5 years after diagnosis.

4.2%
Cancers diagnosed among AYAs, ages 15–39, 4.2%.
5-Year
Relative Survival
New Cancer Cases, 2025
Estimated New Cancers Among AYAs in the U.S. in 2025 85,480
% of All New Cancer Cases at Any Age 4.2%
Common Types of New Cancers Among AYAs
| Breast Cancer | 11.709169282 (15%) |
|---|---|
| Thyroid Cancer | 11.169835695 (15%) |
| Testicular Cancer | 5.975661475 (8%) |
| Melanoma of the Skin | 5.464420449 (7%) |
| Other | 41.868591998 (55%) |
Distribution based on age-adjusted rates of new cases.
SEER 21, 2018–2022.
Cancer Deaths, 2025
Estimated Cancer Deaths Among AYAs the U.S. in 2025 9,380
% of All Cancer Deaths at Any Age 1.5%
Common Cancer Types Causing Death Among AYAs
| Breast Cancer | 1.051066967 (12%) |
|---|---|
| Brain and Other Nervous System (ONS) Cancer | 0.934552002 (11%) |
| Colorectal Cancer | 0.903732159 (11%) |
| Leukemia | 0.801866217 (10%) |
| Other | 4.741290934 (56%) |
Distribution based on age-adjusted death rates.
U.S. Mortality, 2019–2023.
In 2025, it is estimated that there will be 85,480 new cases of cancer among AYAs and 9,380 deaths due to cancer among AYAs.
| Year | Rate of New Cases — SEER 8 | Rate of New Cases — SEER 12 | Death Rate — U.S. | 5-Year Relative Survival — SEER 8 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed | Modeled Trend | Observed | Modeled Trend | Observed | Modeled Trend | Observed | Modeled Trend | |
| 1975 | 58.19 | 58.41 | - | - | 16.45 | 16.08 | 70.34% | 71.22% |
| 1976 | 57.82 | 58.52 | - | - | 16.12 | 15.90 | 72.49% | 71.68% |
| 1977 | 59.75 | 58.64 | - | - | 15.88 | 15.72 | 72.85% | 72.14% |
| 1978 | 58.87 | 58.75 | - | - | 15.25 | 15.55 | 72.23% | 72.59% |
| 1979 | 58.96 | 58.86 | - | - | 15.08 | 15.37 | 72.18% | 73.03% |
| 1980 | 58.77 | 58.97 | - | - | 15.33 | 15.20 | 73.91% | 73.47% |
| 1981 | 59.46 | 60.38 | - | - | 14.68 | 15.03 | 74.07% | 73.91% |
| 1982 | 61.49 | 61.83 | - | - | 14.85 | 14.86 | 74.05% | 73.21% |
| 1983 | 62.61 | 63.31 | - | - | 14.49 | 14.70 | 72.75% | 72.50% |
| 1984 | 65.19 | 64.82 | - | - | 14.64 | 14.53 | 70.29% | 71.78% |
| 1985 | 67.00 | 66.37 | - | - | 14.52 | 14.37 | 70.37% | 71.04% |
| 1986 | 68.79 | 67.96 | - | - | 14.42 | 14.21 | 70.93% | 70.29% |
| 1987 | 70.74 | 69.59 | - | - | 13.91 | 14.05 | 69.15% | 69.52% |
| 1988 | 71.23 | 71.25 | - | - | 13.73 | 13.89 | 67.83% | 68.73% |
| 1989 | 73.01 | 72.96 | - | - | 13.55 | 13.74 | 68.25% | 67.93% |
| 1990 | 73.84 | 74.70 | - | - | 13.59 | 13.58 | 67.83% | 67.12% |
| 1991 | 72.29 | 73.46 | - | - | 13.52 | 13.43 | 68.60% | 68.22% |
| 1992 | 73.54 | 72.24 | 71.38 | 70.06 | 13.38 | 13.28 | 69.02% | 69.29% |
| 1993 | 69.46 | 71.04 | 66.72 | 68.82 | 12.81 | 13.00 | 71.13% | 70.33% |
| 1994 | 69.92 | 69.86 | 67.47 | 67.61 | 12.76 | 12.72 | 72.16% | 71.35% |
| 1995 | 69.89 | 68.70 | 67.69 | 66.42 | 12.53 | 12.44 | 73.47% | 74.29% |
| 1996 | 67.56 | 67.56 | 65.33 | 65.25 | 12.29 | 12.18 | 77.58% | 76.97% |
| 1997 | 66.32 | 66.44 | 63.09 | 64.10 | 12.03 | 11.92 | 79.63% | 79.42% |
| 1998 | 65.02 | 65.33 | 62.39 | 62.97 | 11.80 | 11.66 | 80.43% | 80.17% |
| 1999 | 65.94 | 66.31 | 63.32 | 63.65 | 11.30 | 11.41 | 81.27% | 80.89% |
| 2000 | 67.88 | 67.30 | 64.18 | 64.33 | 11.06 | 11.16 | 81.07% | 81.59% |
| 2001 | 68.18 | 68.31 | 65.06 | 65.02 | 11.11 | 10.92 | 81.81% | 82.27% |
| 2002 | 69.32 | 69.33 | 65.57 | 65.72 | 10.79 | 10.69 | 82.98% | 82.92% |
| 2003 | 71.19 | 70.37 | 66.23 | 66.42 | 10.46 | 10.46 | 83.68% | 83.56% |
| 2004 | 71.74 | 71.42 | 67.72 | 67.13 | 10.06 | 10.23 | 84.48% | 84.17% |
| 2005 | 72.39 | 72.49 | 68.91 | 67.85 | 9.90 | 10.02 | 85.25% | 84.76% |
| 2006 | 71.08 | 73.58 | 68.01 | 68.58 | 9.88 | 9.80 | 84.84% | 85.33% |
| 2007 | 74.50 | 74.68 | 69.91 | 69.32 | 9.49 | 9.59 | 85.48% | 85.89% |
| 2008 | 77.09 | 75.79 | 73.17 | 70.06 | 9.49 | 9.50 | 86.84% | 86.42% |
| 2009 | 76.39 | 76.00 | 71.82 | 70.81 | 9.66 | 9.42 | 86.20% | 86.65% |
| 2010 | 74.75 | 76.21 | 70.47 | 71.57 | 9.33 | 9.33 | 86.63% | 86.88% |
| 2011 | 75.64 | 76.42 | 71.10 | 72.34 | 9.21 | 9.25 | 86.85% | 87.10% |
| 2012 | 76.69 | 76.64 | 73.26 | 73.11 | 9.07 | 9.16 | 87.35% | 87.32% |
| 2013 | 75.39 | 76.85 | 72.05 | 73.90 | 8.99 | 9.08 | 87.64% | 87.54% |
| 2014 | 78.37 | 77.06 | 74.49 | 74.69 | 9.01 | 9.00 | 87.56% | 87.75% |
| 2015 | 78.97 | 77.27 | 75.49 | 75.49 | 8.86 | 8.92 | 88.05% | 87.96% |
| 2016 | 80.46 | 77.49 | 76.44 | 75.47 | 8.98 | 8.84 | 88.66% | 88.17% |
| 2017 | 77.51 | 77.70 | 74.87 | 75.45 | 8.70 | 8.76 | 88.03% | 88.37% |
| 2018 | 76.23 | 77.91 | 74.61 | 75.43 | 8.72 | 8.68 | - | 88.57% |
| 2019 | 78.68 | 78.13 | 75.91 | 75.41 | 8.52 | 8.60 | - | 88.77% |
| 2020 | 72.48 | 78.35 | 70.68 | 75.38 | 8.28 | 8.52 | - | 88.96% |
| 2021 | 78.62 | 78.56 | 76.35 | 75.36 | 8.45 | 8.45 | - | 89.15% |
| 2022 | 77.33 | 78.78 | 74.57 | 75.34 | 8.60 | 8.37 | - | 89.34% |
| 2023 | - | - | - | - | 8.30 | 8.29 | - | - |
Modeled trend lines were calculated from the underlying rates using the Joinpoint Trend Analysis Software.
The 2020 incidence rate is displayed but not used in the fit of the trend line(s). Impact of COVID on SEER Cancer Incidence 2020 data
Using statistical models for analysis, rates of new cancer cases of any site among AYAs have been rising on average 0.3% each year over 2013–2022, the last 10 years of available data. Death rates have been falling on average 0.9% each year over 2014–2023.
Survival Statistics
How Many AYAs Survive 5 Years Or More after Being Diagnosed with Cancer?
Relative survival is an estimate of the percentage of patients who would be expected to survive the effects of their cancer. It excludes the risk of dying from other causes. Because survival statistics are based on large groups of people, they cannot be used to predict exactly what will happen to an individual patient. No two patients are entirely alike, and treatment and responses to treatment can vary greatly.
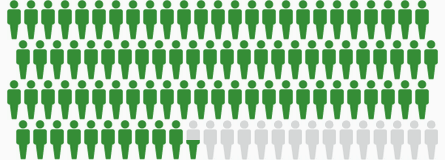
5-Year
Relative Survival
Based on data from SEER 21 (Excluding IL) 2015–2021. Gray figures represent AYAs who have died from cancer within 5 years of diagnosis. Green figures represent those who have survived 5 years or more.
New Cases and Deaths
New Cancers Among AYAs
The most common cancer type among AYAs is female breast cancer, with an age-adjusted rate of 23.6 new cases per 100,000 female AYAs, followed by testicular cancer (11.8 per 100,000 male AYAs) and thyroid cancer (11.2 per 100,000 AYAs). The 10 most common cancers among AYAs represent about 75% of new cancers among AYAs.
Male
| Breast Cancer | 0.096342769 |
|---|---|
| Thyroid Cancer | 4.292093196 |
| Testicular Cancer | 11.764365656 |
| Melanoma of the Skin | 3.734030189 |
| Colorectal Cancer | 5.286302901 |
| Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 4.605107287 |
| Leukemia | 4.238735218 |
| Hodgkin Lymphoma | 3.493196714 |
| Cervical Cancer | 0 |
| Brain and Other Nervous System (ONS) Cancer | 3.161564363 |
Female
| Breast Cancer | 23.632886718 |
|---|---|
| Thyroid Cancer | 18.259151941 |
| Testicular Cancer | 0 |
| Melanoma of the Skin | 7.246218529 |
| Colorectal Cancer | 5.441585865 |
| Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 3.370326931 |
| Leukemia | 3.129944685 |
| Hodgkin Lymphoma | 3.435130953 |
| Cervical Cancer | 6.201220762 |
| Brain and Other Nervous System (ONS) Cancer | 2.396951282 |
Age-adjusted rates of new cases per 100,000. SEER 21, 2018–2022.
Cancer Deaths Among AYAs
Female breast cancer is the deadliest cancer among AYAs with an age-adjusted death rate of 2.1 per 100,000 female AYAs, followed by brain and other nervous system (ONS) cancer (0.9 per 100,000 AYAs) and colorectal cancer (0.9 per 100,000 AYAs). The 10 deadliest cancers among AYAs represent about 70% of cancer deaths among AYAs.
Male
| Breast Cancer | 0.010326657 |
|---|---|
| Brain and Other Nervous System (ONS) Cancer | 1.144645618 |
| Colorectal Cancer | 1.025495378 |
| Leukemia | 0.944062853 |
| Cervical Cancer | 0 |
| Soft Tissue Cancer | 0.468282346 |
| Bone and Joint Cancer | 0.415638245 |
| Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 0.421574128 |
| Lung and Bronchus Cancer | 0.359855993 |
| Stomach Cancer | 0.305425533 |
Female
| Breast Cancer | 2.11396287 |
|---|---|
| Brain and Other Nervous System (ONS) Cancer | 0.718888692 |
| Colorectal Cancer | 0.779157084 |
| Leukemia | 0.655201187 |
| Cervical Cancer | 0.845085381 |
| Soft Tissue Cancer | 0.365954929 |
| Bone and Joint Cancer | 0.258227963 |
| Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 0.223240237 |
| Lung and Bronchus Cancer | 0.283278683 |
| Stomach Cancer | 0.276459581 |
Age-adjusted death rates per 100,000. U.S., 2019–2023.
How Do Cancer Types Among AYAs Compare?
For comparison purposes, new cancer cases (incidence) and cancer deaths (mortality) are generally expressed as rates - that is, the number of new cases (or deaths) per 100,000 persons in the total population. Note that the total population varies depending on which group you are looking at, so, for example, the cancer incidence rate for females is the rate of new cancer cases per 100,000 females in the total population.
The table below gives the rate of new cases and deaths over the most recent five years of data and the five-year relative survival rate, representing the percent surviving their cancer for 5 years after diagnosis.
You can sort on any column by clicking the header to rank the case counts, deaths, incidence and mortality rates, relative survival in ascending or descending order.
| Site | Rate of New Cases (2018–2022) | Death Rate (2019–2023) | 5-Year Relative Survival (%) (2015–2021) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder | 0.6 | 0.0 | 89.4 |
| Bone and Joint | 0.9 | 0.3 | 71.8 |
| Brain and Other Nervous System (ONS) | 2.8 | 0.9 | 72.1 |
| Breast | 11.7 | 1.1 | 87.1 |
| Cervix | 6.2 | 0.8 | 80.6 |
| Colon and Rectum | 5.4 | 0.9 | 75.2 |
| Hodgkin Lymphoma | 3.5 | 0.1 | 96.7 |
| Kidney and Renal Pelvis | 2.5 | 0.1 | 90.1 |
| Leukemia | 3.7 | 0.8 | 74.8 |
| Liver and Intrahepatic Bile Duct | 0.5 | 0.2 | 39.4 |
| Lung and Bronchus | 0.9 | 0.3 | 54.9 |
| Melanoma of the Skin | 5.5 | 0.2 | 96.5 |
| Myeloma | 0.3 | 0.0 | 82.7 |
| Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 4.0 | 0.3 | 86.8 |
| Oral Cavity and Pharynx | 1.4 | 0.1 | 83.2 |
| Ovary | 3.2 | 0.4 | 82.1 |
| Pancreas | 0.7 | 0.2 | 61.2 |
| Small Intestine | 0.4 | 0.0 | 83.5 |
| Soft Tissue | 1.6 | 0.4 | 71.0 |
| Stomach | 1.0 | 0.3 | 40.0 |
| Testis | 11.8 | 0.4 | 95.3 |
| Thyroid | 11.2 | 0.0 | 99.8 |
| Uterus | 4.4 | 0.3 | 90.7 |
| Site | Rate of New Cases (2018–2022) | Death Rate (2019–2023) | 5-Year Relative Survival (%) (2015–2021) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder | 0.3 | 0.0 | 83.8 |
| Bone and Joint | 0.8 | 0.3 | 77.9 |
| Brain and Other Nervous System (ONS) | 2.4 | 0.7 | 76.7 |
| Breast | 23.6 | 2.1 | 87.1 |
| Cervix | 6.2 | 0.8 | 80.6 |
| Colon and Rectum | 5.4 | 0.8 | 78.4 |
| Hodgkin Lymphoma | 3.4 | 0.1 | 97.5 |
| Kidney and Renal Pelvis | 2.0 | 0.1 | 92.0 |
| Leukemia | 3.1 | 0.7 | 76.7 |
| Liver and Intrahepatic Bile Duct | 0.4 | 0.2 | 46.3 |
| Lung and Bronchus | 1.0 | 0.3 | 59.3 |
| Melanoma of the Skin | 7.2 | 0.2 | 97.7 |
| Myeloma | 0.3 | 0.0 | 83.5 |
| Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 3.4 | 0.2 | 89.1 |
| Oral Cavity and Pharynx | 1.3 | 0.1 | 88.5 |
| Ovary | 3.2 | 0.4 | 82.1 |
| Pancreas | 0.9 | 0.2 | 71.9 |
| Small Intestine | 0.4 | 0.0 | 86.0 |
| Soft Tissue | 1.6 | 0.4 | 75.5 |
| Stomach | 1.0 | 0.3 | 44.2 |
| Testis | - | - | - |
| Thyroid | 18.3 | 0.0 | 99.9 |
| Uterus | 4.4 | 0.3 | 90.7 |
| Site | Rate of New Cases (2018–2022) | Death Rate (2019–2023) | 5-Year Relative Survival (%) (2015–2021) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder | 0.8 | 0.0 | 91.8 |
| Bone and Joint | 1.0 | 0.4 | 67.7 |
| Brain and Other Nervous System (ONS) | 3.2 | 1.1 | 68.7 |
| Breast | 0.1 | 0.0 | 85.5 |
| Cervix | - | - | - |
| Colon and Rectum | 5.3 | 1.0 | 72.0 |
| Hodgkin Lymphoma | 3.5 | 0.1 | 95.9 |
| Kidney and Renal Pelvis | 2.9 | 0.2 | 88.7 |
| Leukemia | 4.2 | 0.9 | 73.5 |
| Liver and Intrahepatic Bile Duct | 0.6 | 0.3 | 34.4 |
| Lung and Bronchus | 0.9 | 0.4 | 50.3 |
| Melanoma of the Skin | 3.7 | 0.2 | 94.3 |
| Myeloma | 0.4 | 0.0 | 81.9 |
| Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 4.6 | 0.4 | 85.2 |
| Oral Cavity and Pharynx | 1.5 | 0.2 | 79.0 |
| Ovary | - | - | - |
| Pancreas | 0.6 | 0.2 | 47.8 |
| Small Intestine | 0.4 | 0.0 | 80.7 |
| Soft Tissue | 1.7 | 0.5 | 67.2 |
| Stomach | 0.9 | 0.3 | 35.5 |
| Testis | 11.8 | 0.4 | 95.3 |
| Thyroid | 4.3 | 0.0 | 99.5 |
| Uterus | - | - | - |
Who Gets This Cancer?
The age-adjusted incidence rate among AYAs was 76.2 per 100,000 AYAs per year based on 2018–2022 cases.
Who Dies From This Cancer?
The death rate was 8.4 per 100,000 AYAs per year based on 2019–2023 deaths.
Trends in Rates
Changes Over Time
Keeping track of new cases, deaths, and survival over time (trends) can help scientists understand whether progress is being made and where additional research is needed to address challenges, such as improving screening or finding better treatments.
Interactive Statistics with SEER*Explorer
- Create custom graphs and tables
- Download data and images
- Share links to results
SEER*Explorer is an interactive website that provides easy access to a wide range of SEER cancer statistics. It provides detailed statistics for a cancer site by sex, race, calendar year, age, and for a selected number of cancer sites, by stage and histology.
Explore Additional Cancer Statistics Among AYAsMore About Cancer
More Information
Here are some resources for learning more about cancer.
- Learn more about cancer
- More about risk factors for cancer
- More about symptoms and diagnosis of cancer
- More about treatment options for cancer
- More about clinical trials
- More about cancer prevention
References
All statistics in this report are based on statistics from SEER and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's National Center for Health Statistics. Most can be found within SEER*Explorer.
Suggested Citation
All material in this report is in the public domain and may be reproduced or copied without permission; citation as to source, however, is appreciated.
SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Cancer Among Adolescents and Young Adults (AYAs). National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/aya.html
These stat facts focus on population statistics that are based on the U.S. population. Because these statistics are based on large groups of people, they cannot be used to predict exactly what will happen to an individual patient. To see tailored statistics, browse SEER*Explorer. To see statistics for a specific state, go to the State Cancer Profiles.
The statistics presented in these stat facts are based on the most recent data available, most of which can be found in SEER*Explorer. In some cases, different year spans may be used.
Estimates of new cases and deaths for 2025 are projections made by the American Cancer Society (ACS), based on earlier reported data.
Cancer is a complex topic. There is a wide range of information available. These stat facts do not address causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, follow-up care, or decision making, although links are provided to information in many of these areas.



